In the world of robotics and automation, highly flexible cables play a crucial role. One such cable is the TRVVP shielded drag chain cable.
Introduction to TRVVP Shielded Drag Chain Cable
This cable is primarily used for signal transmission feedback. It is specifically designed for applications that demand continuous bending and twisting. It’s not only suitable for internal machine wiring but also serves as cables for control and power transmission in drag chain systems. Its applications are extensive, spanning across drag chain systems, sensor technology, computer and instrument control equipment, and control engineering. Additionally, it finds use in loading and unloading equipment and can be deployed both indoors and outdoors, even in wet areas.
Key Features of the Cable
Suitability for Long-Term Twisting and High-Speed Movement
The cable is engineered to be suitable for industrial robots and other robotic equipment. It can endure long-term torsion and bending in complex environments and high-strength applications. The modified version of this cable has an impressive ability to withstand continuous, high-strength twisting. In fact, it can undergo more than 10 million times of cyclic torsion while always maintaining a high degree of stability.
High Flexibility and Bend Resistance for Repetitive Motion Equipment
This highly flexible and bend-resistant cable is ideal for a wide range of equipment that requires back-and-forth reciprocating motion and shielding. This includes industrial robots, woodworking machinery, automated production lines, logistics and warehousing equipment, fire systems, lifting applications, CNC machine tools, and the metallurgical industry. These are all areas where automation and intelligent equipment are prevalent.
Upgraded Sheath for Enhanced Durability
The sheath material of the cable has been upgraded. Special high-flexible PVC is used, which offers multiple advantages. It is oil-resistant, abrasion-resistant, waterproof, flame-retardant, and has high and low-temperature resistance. Moreover, it is highly resistant to tensile forces and folding. This upgraded protection significantly enhances the service life of the cable.
Testing the Flex Resistance of the Cable
To test the flex resistance of the drag chain cable, we simulate various conditions of its bending movement. First, we take specimens from the finished product. Then, we fix them in a drag chain experimental setup in the following way:
- The bending radius is set as r = 7.5D, where D is the cable outer diameter.
- The drag chain travelling distance S is set to 60.
- The test is conducted at a top speed of 90 back-and-forth movements per minute.
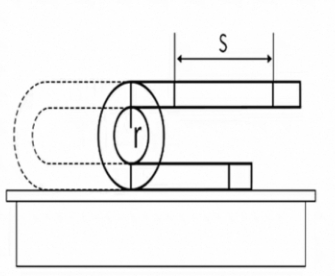
Dynamic bending test: Use special bending test equipment to simulate the bending motion of cables in actual use. Usually set a certain bending frequency, bending angle and stroke, so that the cable in a certain period of time for repeated bending. For example, at a frequency of 50 times per minute, with a bending angle of 180° and a travel distance of 1 metre, 10,000 cyclic bends of the cable are carried out to observe changes in the appearance and performance of the cable.
For example, in a test setup that simulates the movement of a robot arm, the cable is bent while being twisted and stretched to more fully evaluate the cable’s resistance to bending under complex operating conditions. Observe the performance changes and damage of the cables through prolonged simulated operation to determine whether the cables meet the requirements for flexural resistance in actual robot use.
This testing method allows us to accurately assess how well the cable can withstand the rigors of continuous bending and twisting in real-world applications, ensuring that it meets the high standards required for use in robotic and automation systems.
